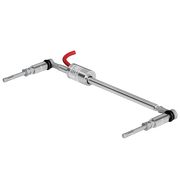
Description:
- Displacement sensor: The vibrating wire displacement sensor can be used in
uniaxial/biaixial/triaxial crack meters or joint meters,
borehole extensometers (BHE) and soil extensometers.
The displacement sensor converts the mechanical
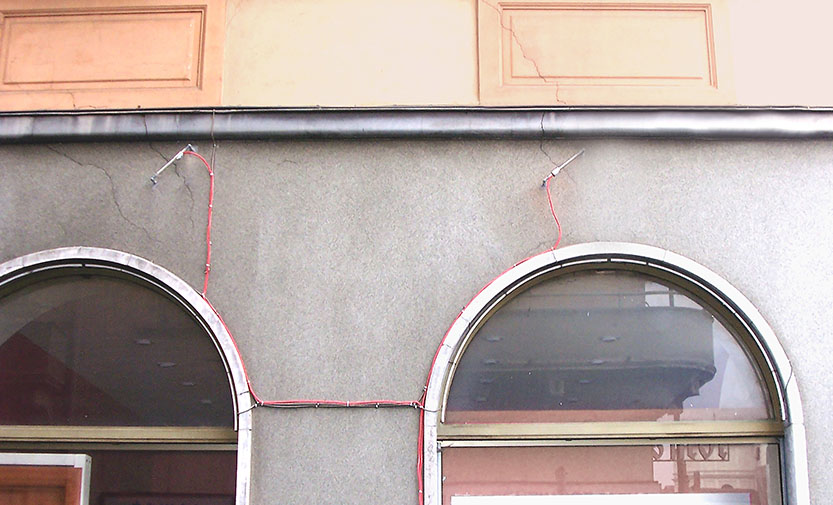
displacement to an electrical frequency output. - The surface jointmeter (also crackmeter or fissurometer) is designed to monitor relative movements of adjacent surfaces across cracks or construction joints.
The surface jointmeter consists of a vibrating wire transducer or a potentiometer, and a set of mounting brackets. - Embedment Joint Meter utilizes a vibrating wire sensor attached to a spring tensioned between two anchors. Any variation of distance between these anchors will change the tension in the wire. The sensor is protected by a sliding stainless steel housing.
Key Features:
- • Rugged, stainless steel body
• Long term reliability and stability
• Quick and easy to read, adaptable to data loggers
or data acquisition system
• ‘O’ ring protection against ingress of moisture
• Unaffected by changes in atmospheric pressure
Applications:
- Structural Health Monitoring: Ensures stability and safety of bridges, tunnels, dams, high-rise buildings, and retaining walls by detecting displacement trends.
- Geotechnical & Mining Applications: Monitors ground settlement, landslides, and subsurface deformations in soil and rock structures.
- Crack & Joint Movement Detection:
- Concrete & Arch Dams: Identifies crack progression and joint expansion.
- Bridges & Pavement Slabs: Detects long-term structural shifts.
- Underground Structures: Monitors tunnel linings and shaft movements.
- Remote & Long-Term Monitoring: Ideal for inaccessible locations where continuous structural assessment is required.