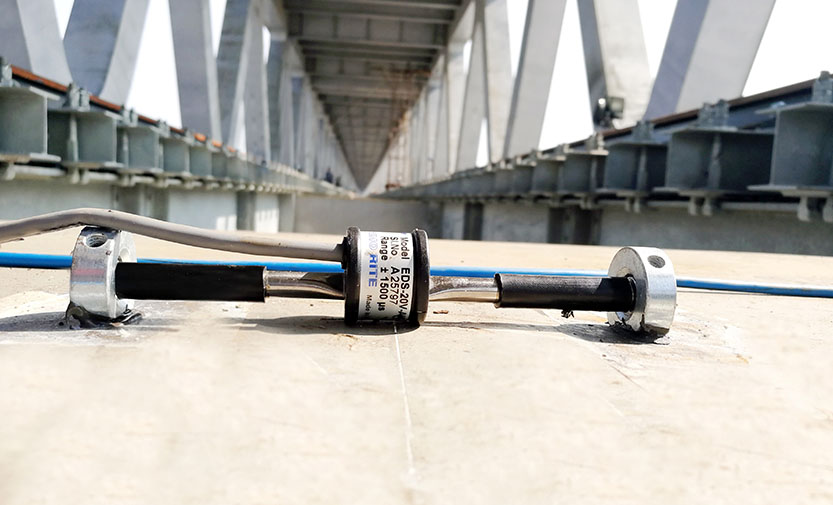
Description:
Strain gages typically consist of a flexible metallic foil mounted on an insulating substrate. When the object to which the gage is attached undergoes deformation, the foil distorts, altering its electrical resistance. This change is then measured to assess the strain in the material. Strain gages are essential for monitoring the structural health of various civil engineering projects, offering vital data on stress distribution and material behavior over time.
Key Features:
- Accurate and reliable: Provides precise strain measurements.
- Versatile: Suitable for use in a wide range of materials like steel, concrete, and rock.
- Long-term stability: Designed for durability in harsh conditions.
- Waterproofing: Many models are hermetically sealed to protect against moisture ingress.
- Stainless steel construction: Ensures robustness and longevity.
- Low cost: High-quality performance at affordable prices.
Applications:
- Concrete and Steel Structures: Monitor strain in dams, bridges, tunnels, and underground cavities.
- Soil and Concrete Embedment: Measure strain in concrete foundations, slurry walls, and piles.
- Stress Distribution: Study stress in tunnel supports, diaphragm walls, and rock formations.
- Pressure Shafts and Steel Structures: Measure strain in pressure shafts and various steel constructions.